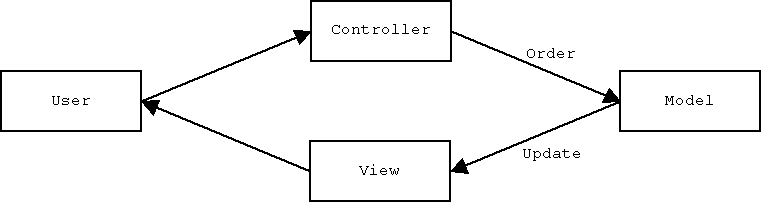
The Model owns the game state.
The Controller stands for the interface the User can manipulate to send orders to modify the game state.
Finally the View reflects how the User perceives the game state.
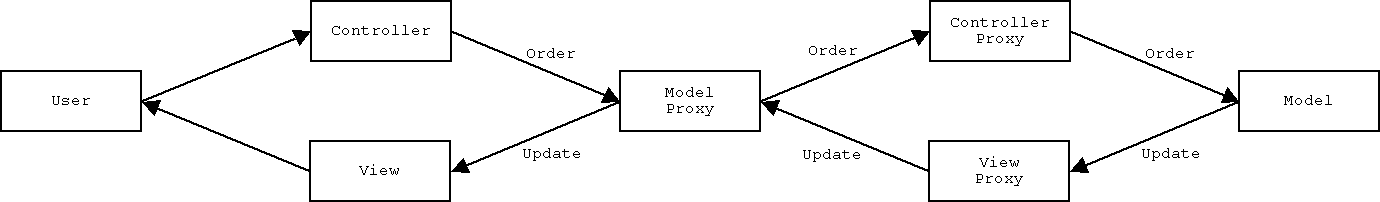
The game state may require to be replicated, hence proxies dealing with the distribution in-between each Controller-Model and Model-View pair are introduced.
Every turn-based game functionalities fall into one of this module.
Security checks are either dynamic or static whether they depend on the game state or not.
Static checks are to be performed by the Controller to avoid forwarding invalid orders to the Model.
Dynamic checks take place within the Model.
The turn processing is definitly to be handled by the Model because it remains tight to the game state.
Depending on the architecture (MVC or Proxy MVC) the three following distributions are possible :
In all cases the Controller and View cope with the distribution.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Model View Controller | MVC description |
| Trinket : Model View Controller pattern | MVC tutorial applied to java applications |
| Model Pipe View Controller | MVC extension with pipes and filters description |
| Model View Presenter | MVP description |